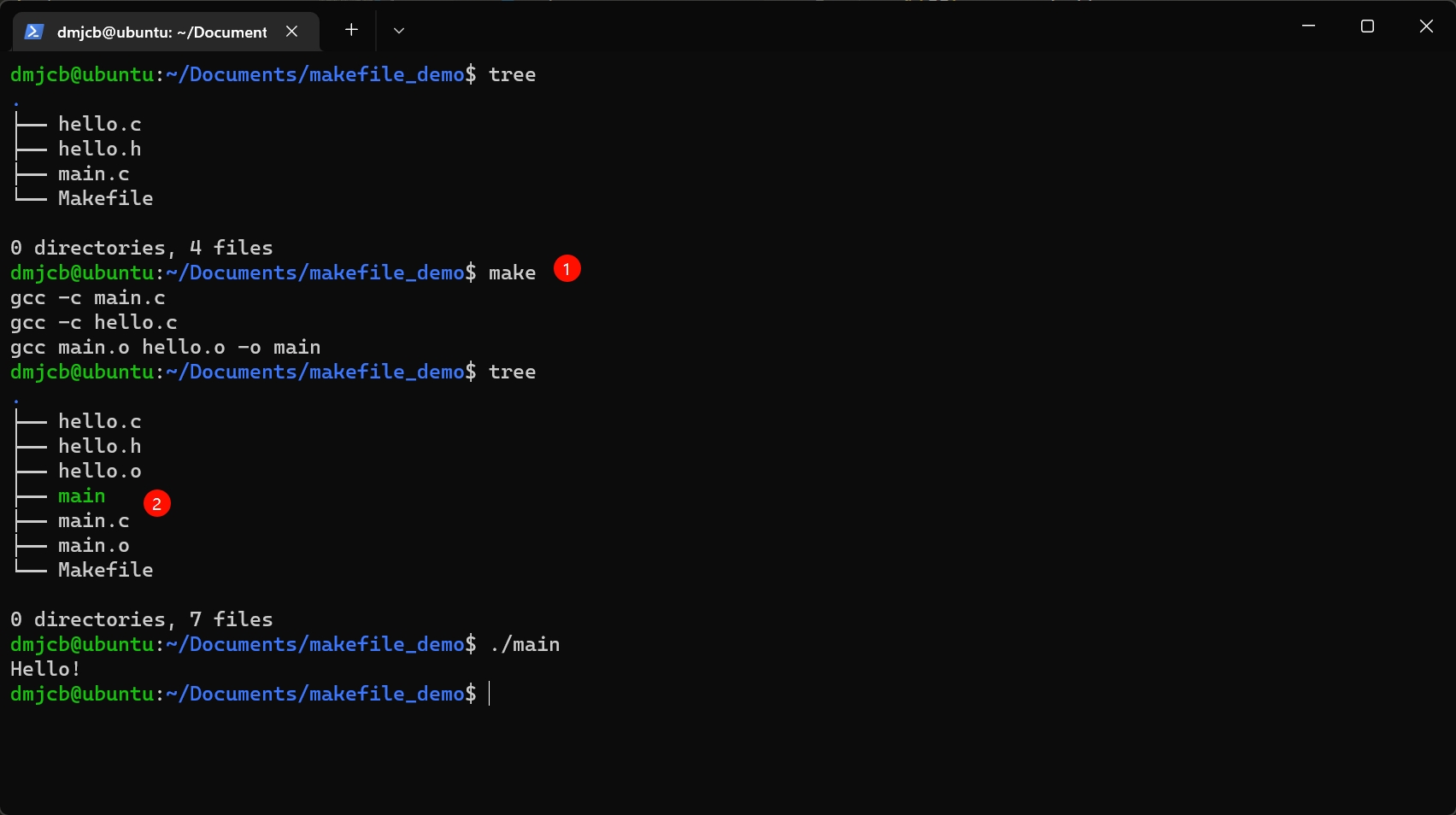
makefile
手动编译
// hello.h
#include <stdio.h>
void Hello();
// hello.c
#include "hello.h"
void Hello() {
printf("Hello!\n");
return;
}
// main.c
#include "hello.h"
int main() {
Hello();
return 0;
}
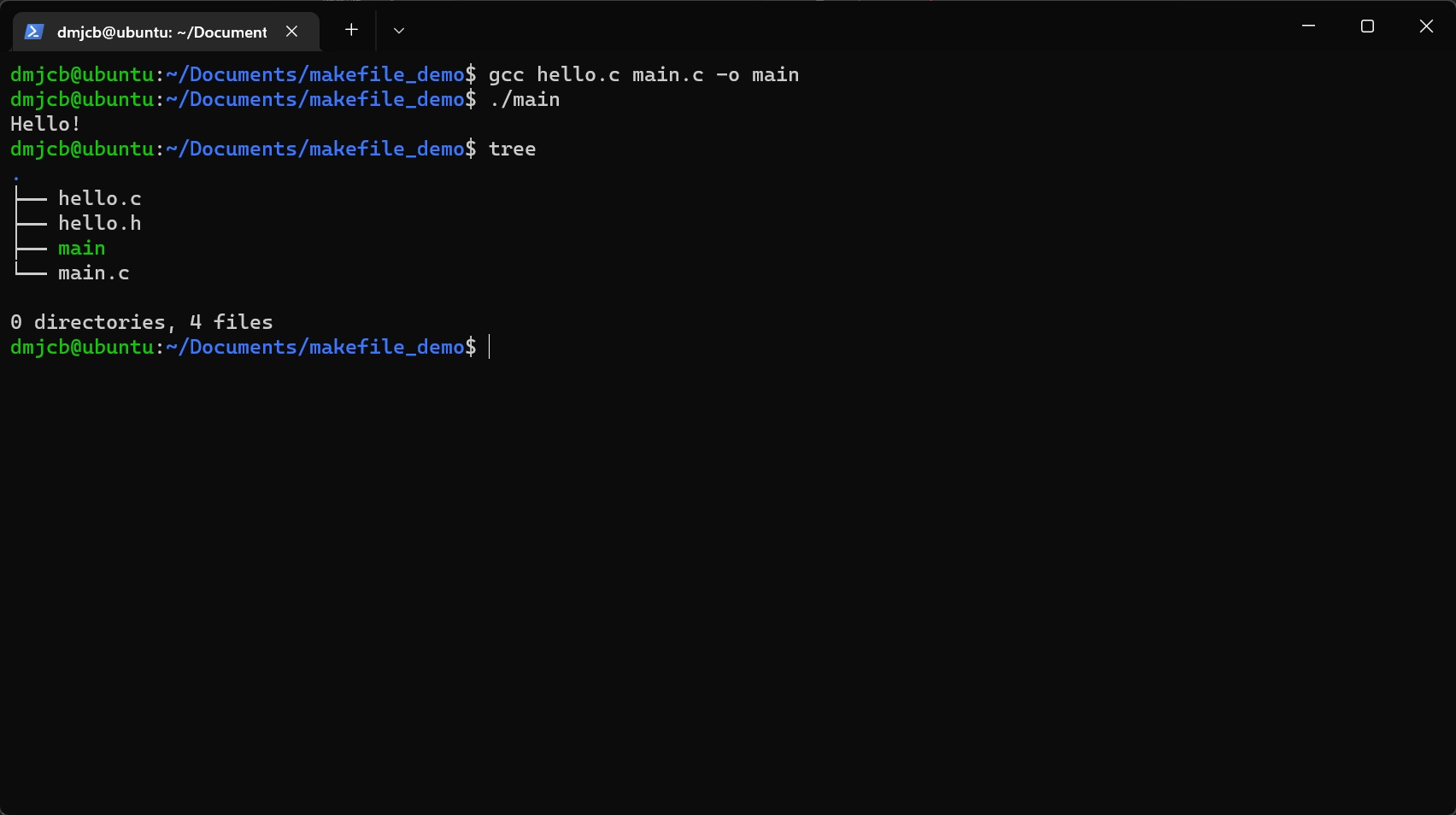
手动编译
gcc hello.c main.c -o main
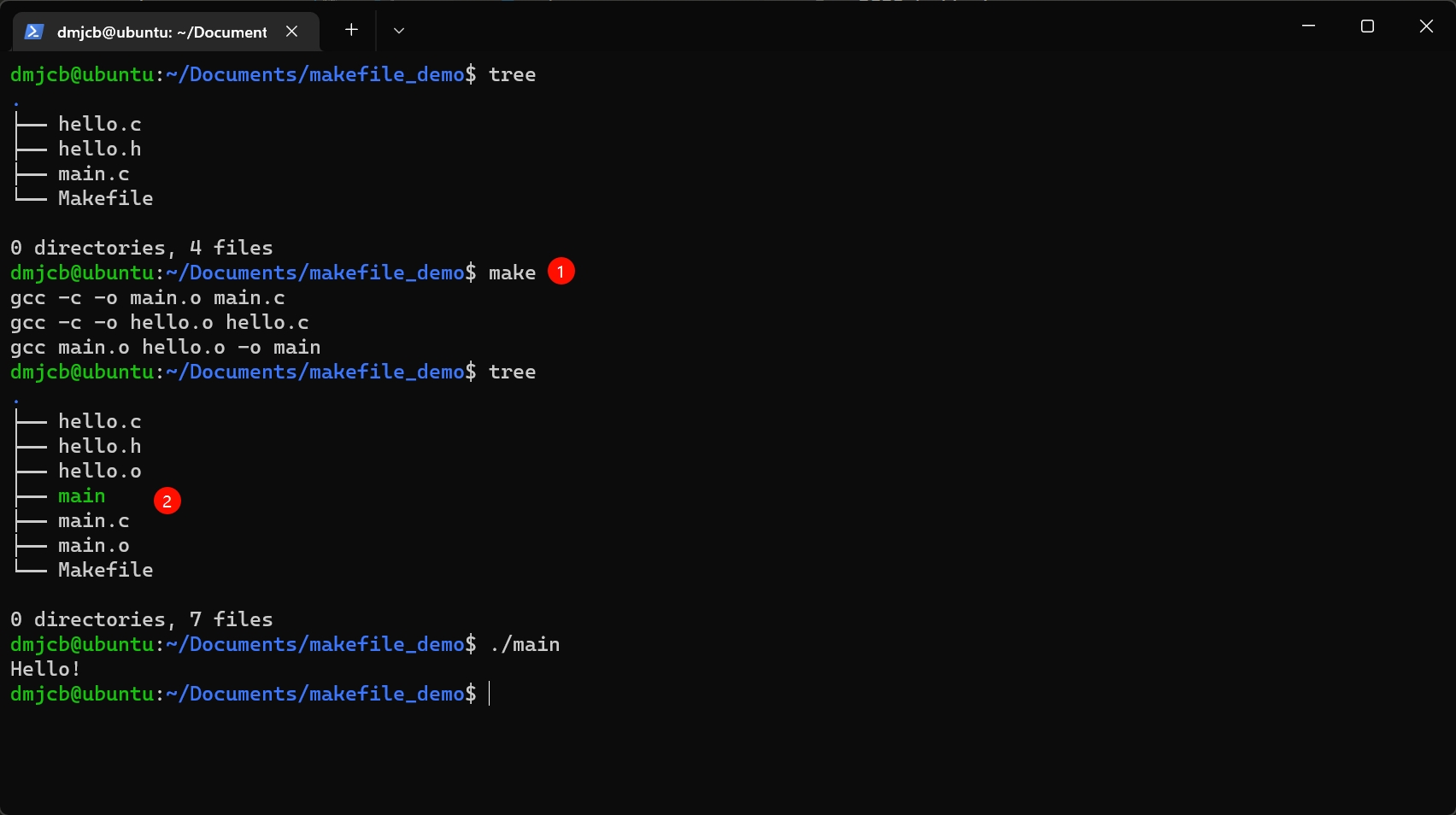
makefile 1
# Makefile
main: main.c hello.c
gcc hello.c main.c -o main
make命令不带参数会默认执行makefile文件中首条规则
通过将命令依赖文件列表放在:之后第一行, 若其中任何文件发生更改, make就会执行main规则
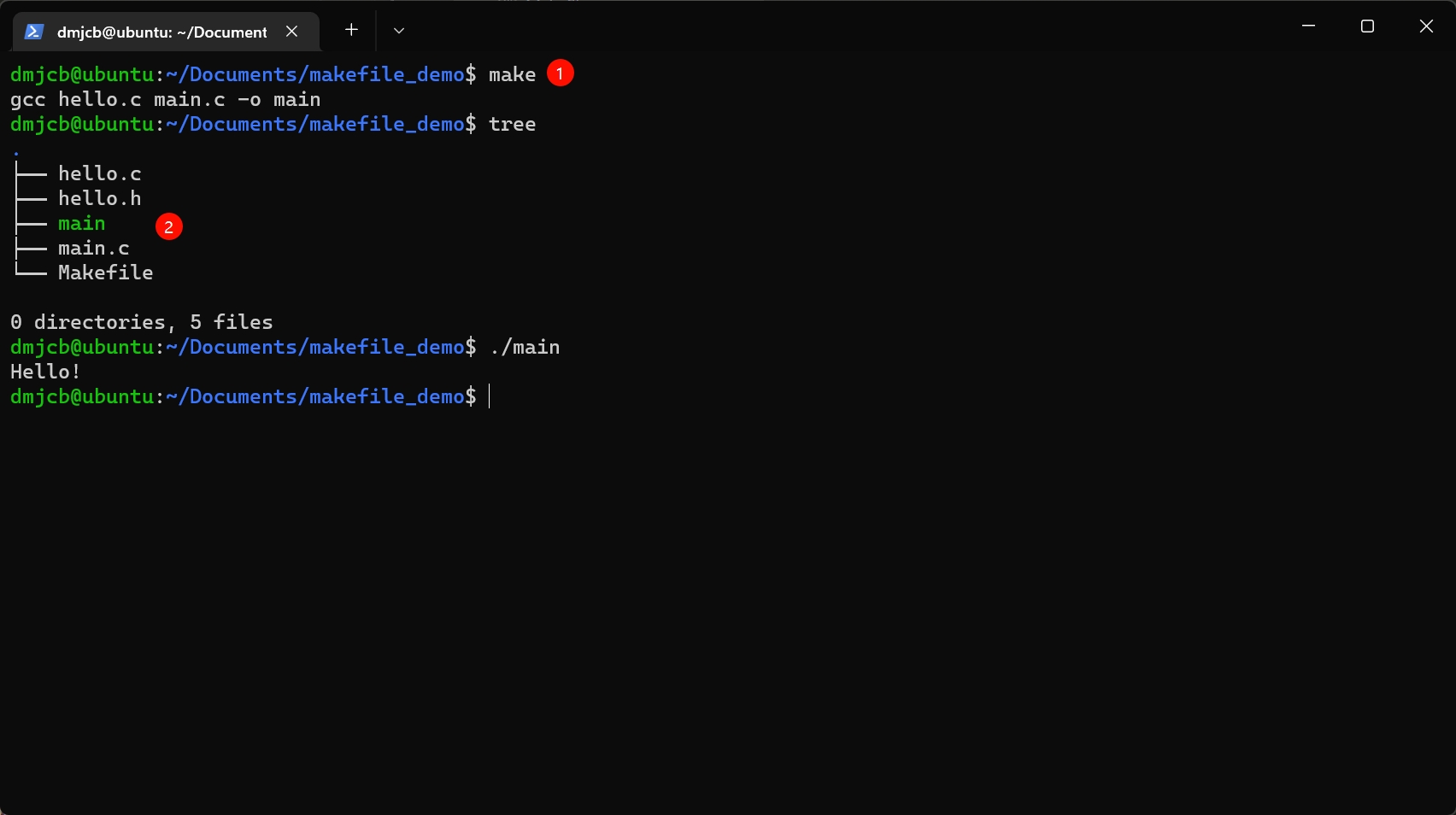
makefile 2
# 定义编译器
CC=gcc
main: main.o hello.o
$(CC) main.o hello.o -o main
hello.o:
$(CC) -c hello.c
main.o:
$(CC) -c main.c
makefile 3
上个版本makefile忽略对头文件依赖, 若修改hello.h, 重新执行make, 并不会重编头文件
此时需告诉make所有.c文件所依赖.h文件
# 定义编译器
CC=gcc
# 依赖头文件
DEPS=hello.h
%.o:%.c $(DEPS)
$(CC) -c -o $@ $<
main: main.o hello.o
$(CC) main.o hello.o -o main
为产生.o文件, make需要使用CC常量定义的编译器编译.c文件
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
$@ |
将输出文件命名为上一行:左边文件名 |
$< |
依赖列表中首项 |
makefile 4
使用特殊宏$@ $^分别表示:左边和右边
# 定义编译器
CC=gcc
# 依赖头文件
DEPS=hello.h
OBJ=main.o hello.o
%.o:%.c $(DEPS)
$(CC) -c -o $@ $<
main: $(OBJ)
$(CC) $^ -o $@